Table of contents
- Introduction
- What Is Metabolic Encephalopathy?
- How Metabolic Encephalopathy Affects the Brain
- Common Causes of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Risk Factors
- Symptoms of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Diagnosis of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Treatment of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Prognosis and Recovery
- Prevention of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 1. Is metabolic encephalopathy reversible?
- 2. How is metabolic encephalopathy different from dementia?
- 3. Can metabolic encephalopathy cause permanent brain damage?
- 4. How long does recovery take?
- 5. Is metabolic encephalopathy life-threatening?
- 6. Can children develop metabolic encephalopathy?
- 7. What tests confirm metabolic encephalopathy?
- Conclusion
Introduction
Metabolic encephalopathy is a serious but often reversible brain disorder caused by systemic metabolic disturbances rather than structural damage to the brain. It occurs when the brain is affected by abnormalities in the body’s chemistry, such as electrolyte imbalances, organ failure, infections, or toxin buildup. Because the brain depends heavily on a stable internal environment, even small metabolic changes can significantly impair mental function.
Metabolic encephalopathy is commonly seen in hospitalized and critically ill patients and can range from mild confusion to deep coma. Early recognition and prompt treatment are crucial, as delayed management may lead to permanent neurological damage or even death. This article provides a comprehensive overview of metabolic encephalopathy, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prognosis, and prevention.
What Is Metabolic Encephalopathy?
Metabolic encephalopathy is a diffuse dysfunction of the brain resulting from metabolic abnormalities in the body. Unlike encephalitis or stroke, it does not involve inflammation or direct injury to brain tissue. Instead, it arises due to disruptions in oxygen delivery, glucose metabolism, toxins, or electrolyte balance.
The condition is considered a type of toxic-metabolic encephalopathy, meaning it is often caused by toxins, metabolic waste, or biochemical imbalances that affect brain function.
How Metabolic Encephalopathy Affects the Brain
The brain requires:
- Continuous oxygen supply
- Stable glucose levels
- Balanced electrolytes
- Efficient removal of toxins
When organs like the liver, kidneys, lungs, or endocrine system fail to maintain these conditions, toxic substances accumulate or energy production becomes impaired. As a result, neurotransmission is disrupted, leading to altered mental status.
Common Causes of Metabolic Encephalopathy
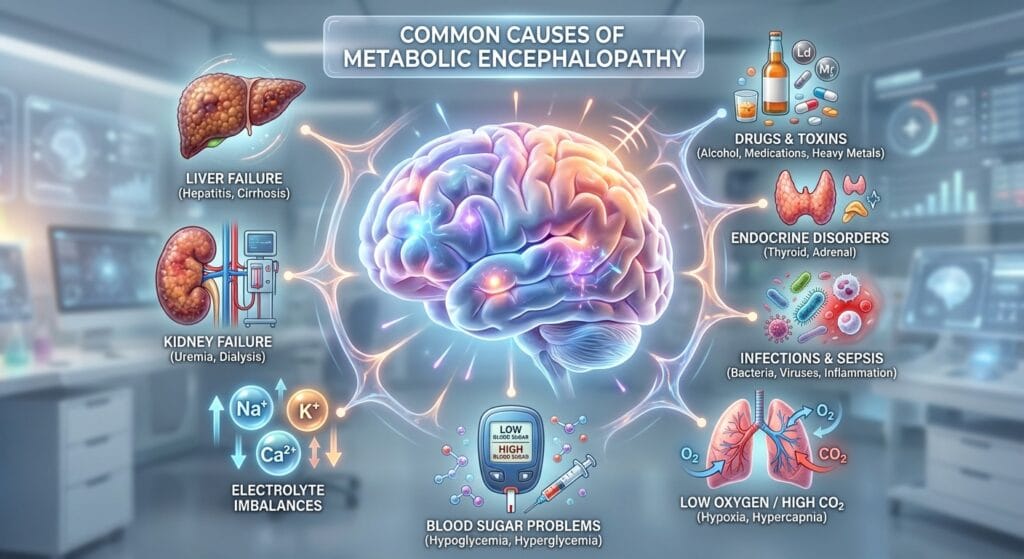
Metabolic encephalopathy has many underlying causes, often classified by the affected metabolic system.
1. Liver Failure (Hepatic Encephalopathy)
- Accumulation of ammonia and other toxins
- Common in cirrhosis and acute liver failure
- Causes confusion, personality changes, and coma
2. Kidney Failure (Uremic Encephalopathy)
- Buildup of urea and nitrogenous waste
- Occurs in chronic kidney disease or acute renal failure
- Symptoms improve with dialysis
3. Electrolyte Imbalances
- Low or high sodium (hyponatremia / hypernatremia)
- Calcium or magnesium imbalance
- Can cause seizures, confusion, and lethargy
4. Hypoglycemia or Hyperglycemia
- Low blood sugar damages brain cells
- High blood sugar may cause hyperosmolar states
- Common in diabetic patients
5. Hypoxia and Hypercapnia
- Low oxygen levels (respiratory failure)
- High carbon dioxide levels
- Seen in COPD, asthma, or pneumonia
6. Infections and Sepsis
- Systemic infections release inflammatory toxins
- Sepsis-associated encephalopathy is common in ICU patients
7. Endocrine Disorders
- Thyroid dysfunction (hypothyroidism or thyroid storm)
- Adrenal insufficiency
8. Drug and Toxin Exposure
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Sedatives, opioids, or chemotherapy drugs
- Heavy metals (lead, mercury)
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at higher risk of developing metabolic encephalopathy, including:
- Elderly patients
- Individuals with chronic liver or kidney disease
- Diabetics
- ICU and post-surgical patients
- Alcohol-dependent individuals
- Patients on multiple medications
Symptoms of Metabolic Encephalopathy
Symptoms vary depending on severity and cause, but generally affect mental status, behavior, and consciousness.
Early Symptoms
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Confusion
- Mood changes
- Sleep disturbances
Moderate Symptoms
- Disorientation (time, place, person)
- Slurred speech
- Tremors or asterixis (flapping hands)
- Hallucinations
Severe Symptoms
- Seizures
- Stupor
- Coma
- Abnormal reflexes
- Respiratory depression
⚠️ Symptoms may develop rapidly or gradually, making early detection challenging.
Diagnosis of Metabolic Encephalopathy
Diagnosis focuses on identifying the underlying metabolic cause rather than brain imaging alone.
Clinical Evaluation
- Detailed medical history
- Medication review
- Assessment of mental status (Glasgow Coma Scale)
Laboratory Tests
- Blood glucose
- Electrolytes
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
- Arterial blood gases
- Ammonia levels
- Thyroid function tests
Imaging Studies
- CT or MRI to rule out stroke, bleeding, or tumors
- Usually normal in metabolic encephalopathy
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Shows generalized slowing
- Helps differentiate from seizures or structural disorders
Treatment of Metabolic Encephalopathy
The cornerstone of treatment is correcting the underlying cause.
1. Supportive Care
- Airway and oxygen support
- IV fluids
- Monitoring vital signs
- Nutritional support
2. Treating the Root Cause
- Dialysis for kidney failure
- Lactulose and rifaximin for hepatic encephalopathy
- Insulin or glucose correction
- Antibiotics for infections
- Electrolyte replacement or correction
3. Medication Adjustment
- Discontinuation of offending drugs
- Dose adjustment in renal or liver disease
4. ICU Management (Severe Cases)
- Mechanical ventilation
- Continuous EEG monitoring
- Management of seizures
Prognosis and Recovery
The prognosis of depends on:
- Speed of diagnosis
- Severity of metabolic disturbance
- Patient’s age and comorbidities
Good Prognosis
- Early treatment
- Reversible causes
- Mild to moderate symptoms
Poor Prognosis
- Delayed intervention
- Severe organ failure
- Prolonged coma
Many patients recover fully once the metabolic imbalance is corrected, but some may experience long-term cognitive impairment, especially elderly patients.
Prevention of Metabolic Encephalopathy
Prevention focuses on managing chronic illnesses and avoiding metabolic disturbances.
- Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function
- Proper diabetes control
- Adequate hydration
- Avoid alcohol abuse
- Medication review and dose adjustment
- Prompt treatment of infections
When to Seek Medical Help
Immediate medical attention is required if a person experiences:
- Sudden confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Severe behavioral changes
- Unexplained drowsiness
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is metabolic encephalopathy reversible?
Yes, in most cases metabolic encephalopathy is reversible if the underlying cause is identified and treated promptly.
2. How is metabolic encephalopathy different from dementia?
Metabolic encephalopathy is usually acute and reversible, while dementia is chronic, progressive, and irreversible.
3. Can metabolic encephalopathy cause permanent brain damage?
If untreated or prolonged, it can lead to permanent neurological impairment, especially in severe cases.
4. How long does recovery take?
Recovery can range from hours to weeks depending on the cause and severity.
5. Is metabolic encephalopathy life-threatening?
Yes, severe cases can be fatal without prompt treatment.
6. Can children develop metabolic encephalopathy?
Yes, especially due to infections, hypoglycemia, or inherited metabolic disorders.
7. What tests confirm metabolic encephalopathy?
Blood tests, EEG, and clinical assessment are key; imaging is used to rule out other causes.
Conclusion
Metabolic encephalopathy is a serious but often treatable neurological condition caused by systemic metabolic disturbances. Early recognition, rapid diagnosis, and targeted treatment are essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes. By managing chronic diseases, monitoring metabolic health, and seeking timely medical care, the risk of can be significantly reduced.