F-16 Engine Maintenance: Complete Guide to Procedures and Best Practices

Introduction
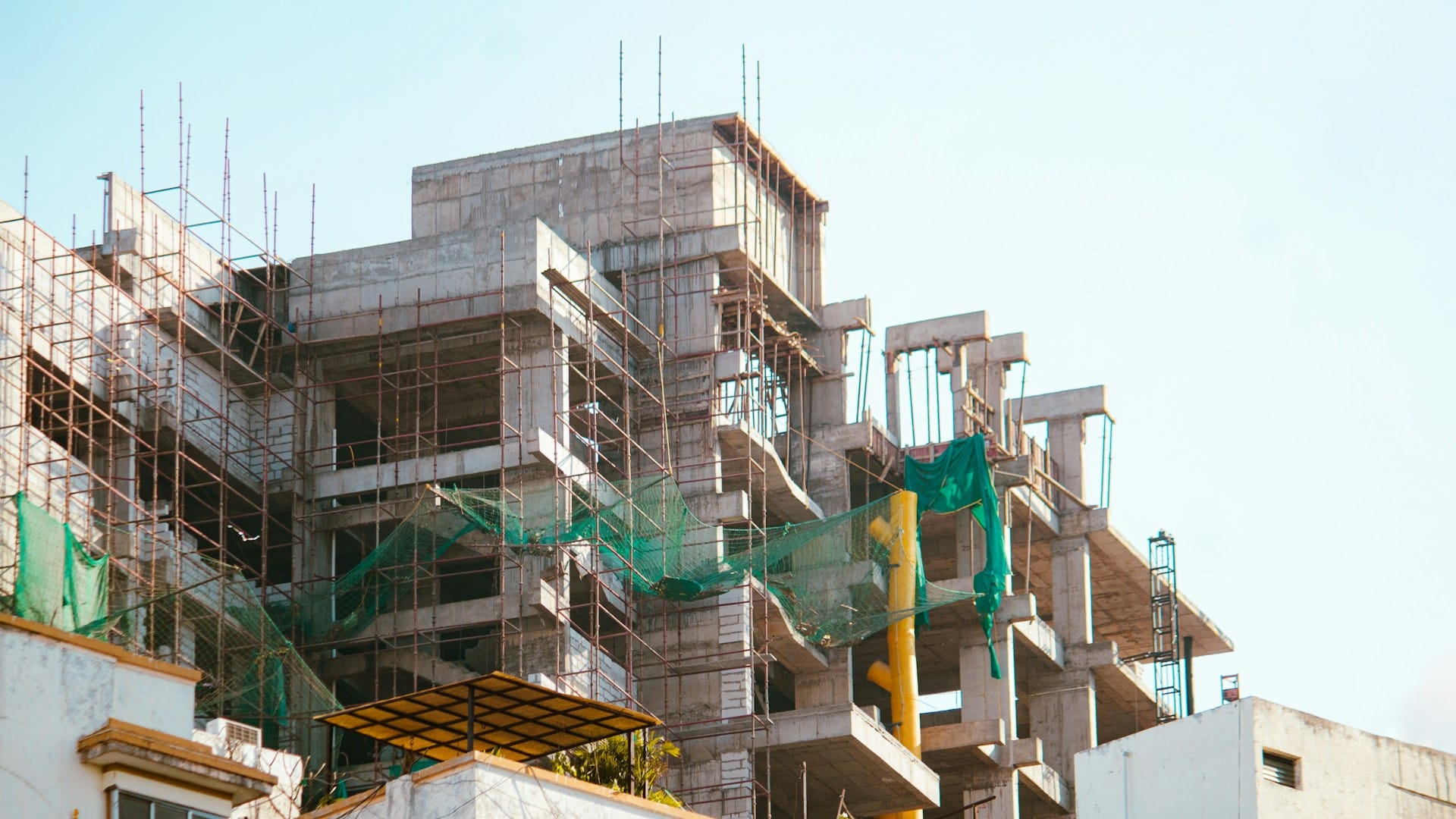
The F-16 Maintenance Fighting Falcon is one of the most widely used multirole fighter aircraft in the world. Known for its agility, reliability, and combat performance, the F-16’s success is closely tied to the health and reliability of its engine. Proper F-16 engine maintenance is essential not only for operational readiness but also for safety, longevity, and cost control.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Overview of F-16 Engines
- Importance of Engine Maintenance in the F-16
- F-16 Engine Maintenance Philosophy
- Key Engine Maintenance Procedures (High-Level Overview)
- Best Practices for F-16 Engine Maintenance
- Common Challenges in F-16 Engine Maintenance
- Role of Technology in Modern Engine Maintenance
- Safety and Compliance Considerations
- Future Trends in F-16 Engine Maintenance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Overview of F-16 Engines
The F-16 platform has primarily operated with two engine families:
- Pratt & Whitney F100 series
- General Electric F110 series
Both engines are afterburning turbofan engines designed to deliver high thrust, rapid throttle response, and sustained performance under extreme flight conditions. While the designs differ, their maintenance philosophies share common principles such as preventive inspections, modular replacement, and strict documentation.
Importance of Engine Maintenance in the F-16
1. Flight Safety
Engine reliability is a critical safety factor. Even minor degradation can lead to reduced thrust, increased fuel consumption, or in rare cases, engine shutdown. Maintenance programs aim to detect issues long before they become safety risks.
2. Mission Readiness
Air forces depend on high aircraft availability rates. A well-maintained F-16 engine ensures quick turnaround times and consistent mission capability.
3. Cost Efficiency
Engines are among the most expensive components of the aircraft. Preventive maintenance significantly reduces long-term costs by avoiding catastrophic failures and extending service life.
F-16 Engine Maintenance Philosophy
F-16 engine maintenance follows a preventive and predictive approach, supported by data, inspections, and condition monitoring.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance focuses on routine checks performed at scheduled intervals. These inspections are designed to identify wear, contamination, or performance degradation early.
Condition-Based Maintenance
Modern F-16 fleets increasingly rely on condition-based maintenance, using performance trends and operational data to determine maintenance needs rather than relying solely on fixed schedules.
Modular Design Advantage
F-16 engines are designed with modular components, allowing maintainers to replace specific sections instead of overhauling the entire engine. This reduces downtime and logistical burden.
Key Engine Maintenance Procedures (High-Level Overview)
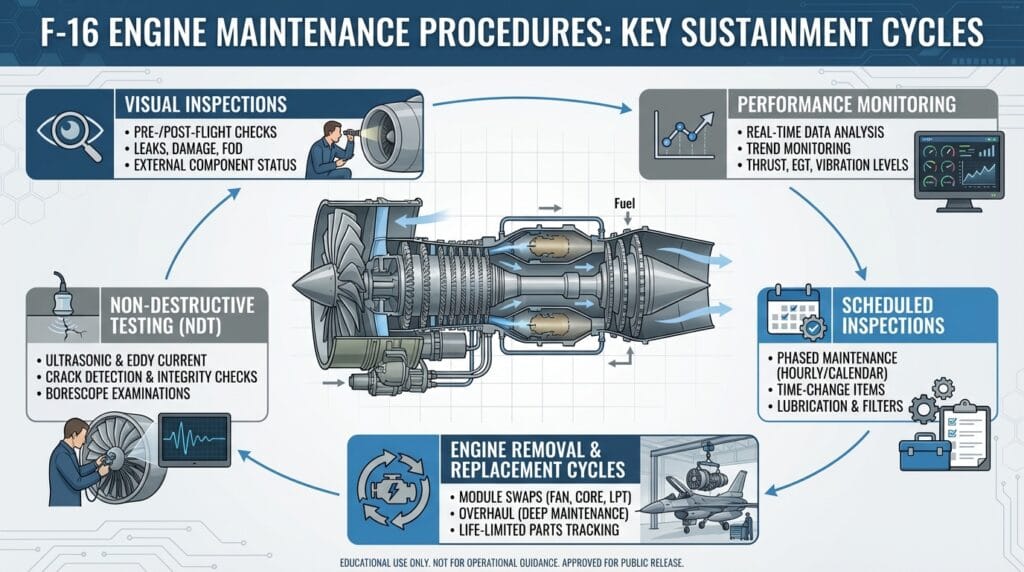
Note: The following sections describe maintenance activities conceptually and do not include technical instructions or operational steps.
Visual Inspections
Regular visual inspections help identify:
- External damage
- Fluid leaks
- Foreign object debris (FOD)
- Abnormal discoloration or residue
These inspections are often the first line of defense against unexpected engine issues.
Performance Monitoring
Engine parameters such as temperature margins, vibration trends, and fuel efficiency are continuously monitored. Deviations from established norms can indicate internal wear or developing faults.
Scheduled Inspections
Maintenance schedules are based on:
- Flight hours
- Operating environment
- Mission profiles
Engines operating in sandy, salty, or high-temperature environments typically require more frequent inspections.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Advanced inspection techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic analysis are used to detect internal cracks or fatigue without disassembling major components.
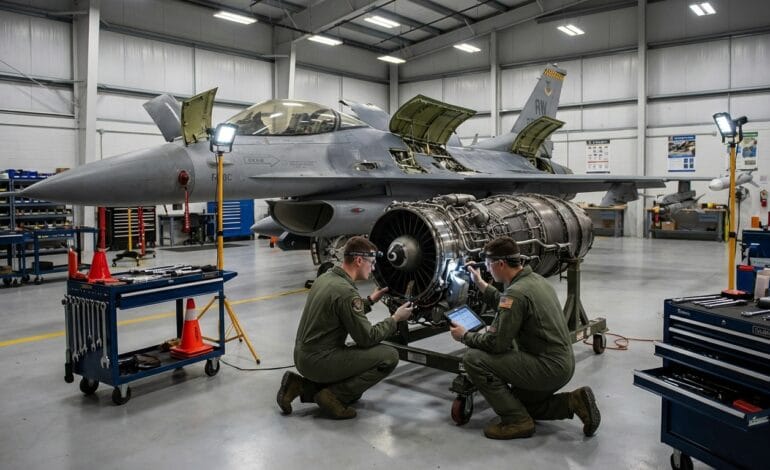
Engine Removal and Replacement Cycles
Rather than repairing engines on the aircraft, F-16 programs often remove engines and replace them with serviceable units. Removed engines are then inspected and serviced in controlled maintenance facilities.
Best Practices for F-16 Engine Maintenance
1. Strict Documentation
Every inspection, trend analysis, and component change must be documented. Accurate records support safety investigations, fleet planning, and regulatory compliance.
2. FOD Prevention Programs
Foreign object damage is one of the most common threats to jet engines. Best practices include:
- Clean ramp environments
- Tool accountability systems
- Pre- and post-flight area inspections
3. Environmental Adaptation
Maintenance strategies should reflect local operating conditions. Engines in desert regions face erosion and sand ingestion risks, while maritime environments increase corrosion concerns.
4. Skilled Personnel Training
Human expertise remains a cornerstone of engine maintenance. Continuous training ensures personnel stay updated with evolving systems, materials, and diagnostic tools.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Modern maintenance programs use engine health monitoring systems to anticipate problems, allowing maintainers to act before failures occur.
Common Challenges in F-16 Engine Maintenance
Aging Fleets
Many F-16s have exceeded their original design life. Aging engines require enhanced inspection regimes and careful life-extension planning.
Supply Chain Constraints
Spare parts availability can impact maintenance schedules. Effective inventory planning is critical to avoid aircraft downtime.
Operational Tempo
High operational demand accelerates wear. Balancing mission requirements with maintenance capacity is an ongoing challenge for operators.
Role of Technology in Modern Engine Maintenance
Digital Maintenance Records
Digital systems improve accuracy, traceability, and data sharing across maintenance units.
Predictive Analytics
Advanced analytics help identify subtle performance changes that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Remote Diagnostics
Some fleets use secure data transmission to allow experts to analyze engine performance without physical access to the aircraft.
Safety and Compliance Considerations
F-16 engine maintenance is governed by:
- Military airworthiness authorities
- Manufacturer technical guidance
- National and international safety standards
Compliance ensures consistent maintenance quality across fleets and countries.
Future Trends in F-16 Engine Maintenance
- Increased automation in inspections
- Expanded use of artificial intelligence for diagnostics
- Greater focus on sustainability and lifecycle cost reduction
- Integration with next-generation maintenance platforms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Maintenance frequency depends on flight hours, operating conditions, and engine type. Regular inspections occur throughout the engine’s service life.
Most fleets use a replace-and-repair approach, where engines are swapped out and serviced in specialized facilities.
Foreign object damage and environmental wear are among the most common risks.
Yes, many engines receive performance and reliability upgrades during scheduled maintenance cycles.
Accurate records ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term fleet planning.
Conclusion
F-16 engine maintenance is a complex, highly regulated discipline that plays a vital role in aircraft safety, mission readiness, and cost efficiency. By following preventive maintenance philosophies, leveraging data-driven insights, and applying best practices, operators can extend engine life while maintaining peak performance.
As technology evolves, F-16 engine maintenance continues to shift toward predictive and condition-based models—ensuring this iconic fighter remains operational for decades to come.
External Backlink
For official aircraft and program information, visit Lockheed Martin’s F-16 Fighting Falcon program:
👉 https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/products/f-16.html